All engineering disciplines involve problem-solving and aim to enhance life in various ways, and the key is to discover which engineering-related solution ignites the most enthusiasm. You'll find staying motivated and engaged throughout your academic and professional journey easier by aligning your studies and future career with your natural interests.
With its various branches and threads, engineering presents a challenge when choosing the right path. Thus, it's crucial to identify one's passions and interests to help in this decision-making process. What excites you, and where do you naturally invest your free time?
Learn more about the different types of engineering degrees in the UK below and begin your application by arranging a free consultation with SI-UK today. We can help you select the right programme from the thousands available in the UK.
Which Type of Engineering Degree Should I Study?
Let's explore some major branches of engineering to assist you in making an informed decision based on your passions and aspirations.
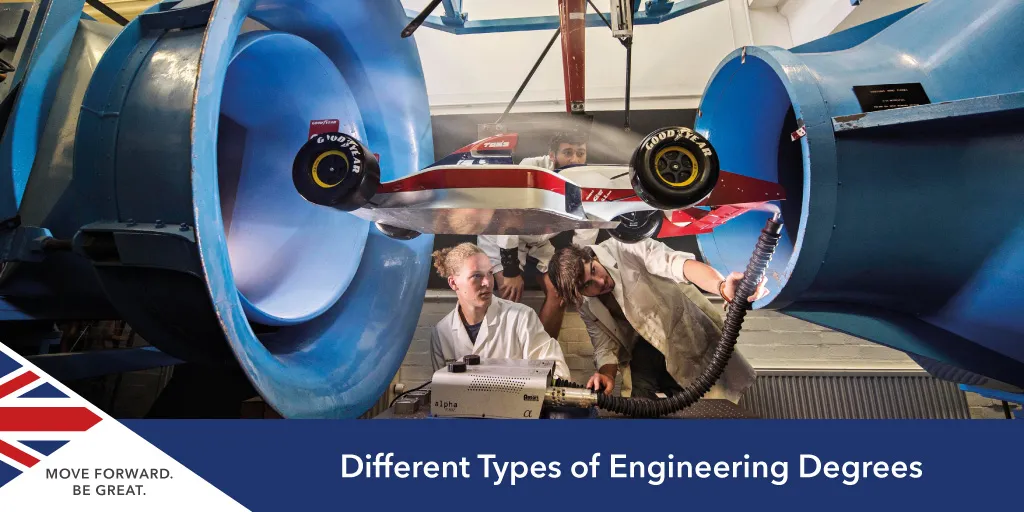
1. Aerospace Engineering Course
- Focuses on aircraft research, design, and development, including astronautical engineering for spacecraft and space conditions.
- Ideal for those captivated by the history and methodology of flying machines, as well as the mechanics of flight travel.
- Suited for individuals intrigued by computer simulations and the performance of aircraft machinery under extreme conditions.
2. Chemical Engineering Course
- Involves using chemical and biological processes to produce useful materials or substances.
- A multidisciplinary field combining natural and experimental sciences, life sciences, mathematics, and economics.
- Ideal for those with an analytical mindset interested in the chemical processes behind everyday items.
3. Civil Engineering Course
- Encompasses the design and development of infrastructure projects on varying scales, from nationwide transport systems to single roads or buildings.
- Suited for individuals interested in designing and building things, focusing on mechanics, hydraulics, geotechnics, materials science, and statistical analysis.
- Offers specialisations in structural engineering, architectural engineering, transportation engineering, environmental engineering, and hydraulic engineering.
4. Computer Engineering Course
- Involves the design and prototyping of computing hardware and software, merging electrical engineering with computer science.
- Ideal for those interested in an engineering career related to computers, mathematics, science, and producing new products based on technological advances.
- Specialisations include microprocessor/microcontroller systems, computer architecture, and VHDL design.
5. Electrical/Electronic Engineering Course
- Focuses on electrical power applications, with electrical engineers emphasising large-scale production and supply, while electronics engineers work on smaller electronic circuits.
- Suited for individuals interested in understanding how electrical devices and systems work and contributing to technological developments.
- Specialisations include power generation and supply, communications and media, and computer and robotic systems.
6. Mechanical Engineering Course
- Deals with mechanical system design, manufacturing, and maintenance, covering statics and dynamics, thermodynamics, fluid dynamics, stress analysis, and technical drawing.
- Suited for those who enjoy working with mechanical devices and want to contribute to fields like sustainable energy and artificial intelligence.
- Common specialisations include manufacturing, transportation systems, combustion, nanotechnology, and robotics.
7. Engineering Management Course
- An interdisciplinary field that combines industrial engineering skills with business expertise.
- Ideal for those interested in understanding how engineering is applied in different business contexts and who want to take on managerial roles.
- Specialisations include engineering mathematics, management science, operations management, decision engineering, business statistics, and engineering statistics.
8. Biomedical Engineering Course
- Combines coursework in technology and medicine to develop equipment enhancing health, like heart monitors and mobility devices.
- Focuses on improving human tissue functionality through expertise in mathematics, biomechanics, and regenerative medicine.
- Ideal for those passionate about merging technology and medicine to contribute to healthcare advancements.
9. Agricultural Engineering Course
- Involves applying engineering principles to the agricultural industry, supporting various facets of farming.
- Focuses on enhancing farming methods, including land preparation, crop growth, harvesting, and storage, with a keen emphasis on soil conservation and irrigation.
- Ideal for individuals interested in the intersection of engineering and agriculture with a desire to contribute to sustainable farming practices.
10. Systems Engineering Course
- Involves studying systems to understand how components collaborate to achieve specific goals or creations.
- Coursework incorporates scientific, technological, and mechanical concepts to foster a comprehensive understanding of systems.
- Ideal for individuals fascinated by the interplay of components within a system and motivated to optimise processes.
Choosing an Engineering Degree Type
1. Identify Your Interests and Skills
Identify your passions and strengths to align with an engineering discipline. Consider self-assessments, academic performance, and teacher feedback to determine your aptitude.
2. What You Need
Assess professional goals, preferred industries, salary requirements, and values to align your career with your aspirations.
3. Research Well
Research potential engineering disciplines, exploring career options, job outlook, and programme details, including entry requirements and tuition.
4. Professional Advice
Connect with experienced engineers to gain insights into different disciplines. Seek guidance from advisors, career counselling services, or professionals within your network.
5. Gain Industry Experience
Participate in internships or shadow programmes to gain practical experience and assess your interest in a specific engineering discipline.
Study Engineering in the UK
Are you aspiring to study a postgraduate or undergraduate engineering degree in the UK? Arrange a free consultation online or at one of our offices today, and we can help you choose from the thousands of engineering degrees available to study in the UK.
http://
FAQ
What is the best engineering degree to study in the UK?
The best engineering degree depends on what you enjoy. If you like building and designing aircraft, aerospace engineering is great. If you're interested in technology and health, biomedical engineering could be the one. Think about what excites you the most.
Which is the toughest engineering course in the UK?
Electrical engineering is considered one of the most challenging engineering subjects to study. It involves understanding energy and technology.
What is the best university in the UK for engineering?
Top engineering universities include Imperial College London, the University of Cambridge, and the University of Oxford. The best one depends on your preferences, like location and specific engineering field.
Is there a shortage of engineers in the UK?
There is a need for more engineers in the UK. Industries like technology, healthcare, and construction require skilled engineers. So, studying engineering can open doors to exciting opportunities and help fill this gap!


.jpg)
